What are we trying to do ?
- Run MySQL as a docker container in Local
- Connecting to it from command line.
- Connecting to it from DBeaver.
What should we have already ?
Select a Web Site. Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select:. Enter values for authentication credentials and other properties required to connect to MySQL. The Server and Port properties must be set to a MySQL server. If IntegratedSecurity is set to false, then User and Password must be set to valid user credentials. Optionally, Database can be set to connect to a specific database.
- DBeaver (Or any other Application that you use to connect to MySQL)
- Step-by-step guide on how to connect to SQL Server using DBeaver on a Mac. Screenshots included. DBeaver is a database management tool for managing DBs such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, SQLite, Oracle, DB2, SQL Server, Sybase, MS Access, Teradata, Firebird, Derby, etc.
- DBeaver is a universal database management tool for everyone who needs to work with data in a professional way. With DBeaver you are able to manipulate with your data like in a regular spreadsheet, create analytical reports based on records from different data storages, export information in an appropriate format.
How can I start ?

RUNNING MYSQL IMAGE IN LOCAL
Run the following command (only after reading the explanation below and substituting it with your own values)
Lets breakdown this command into parts
- docker :- The command to invoke docker
- run :- To create a docker container uses the mysql at the end to determine which docker image it should run. if mysql image is not available in local the latest will be downloaded from docker hub.
- -p :- Tells to map the port 3306 of localhost to 3306 port of the container
- –name :- Sets the name of the container
- -e :- Sets the environment variable. In this case sets the MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
- -d :- Tells to run docker as detcached (not attached to the current terminal but in background)
CHECK IF IT IS RUNNING IN LOCAL
You can see a list of running containers using the following command
CONNECT TO MYSQL IN CONTAINER VIA COMMAND LINE
1. Open the command line inside the container using the following command.
docker exec -it <containername> /bin/sh
2. Type the following commands to login to the instance
3. Enter the password to login
4. If every thing went well we will see that the cursor is mysql>
5. Type some commands to test it.
CONNECT TO MYSQL IN CONTAINER WITH DBEAVER
Client_plugin_auth Is Required Dbeaver Mysql File
1. Open Dbeaver
2. Add a new Connection
3. Select MySQL from the list

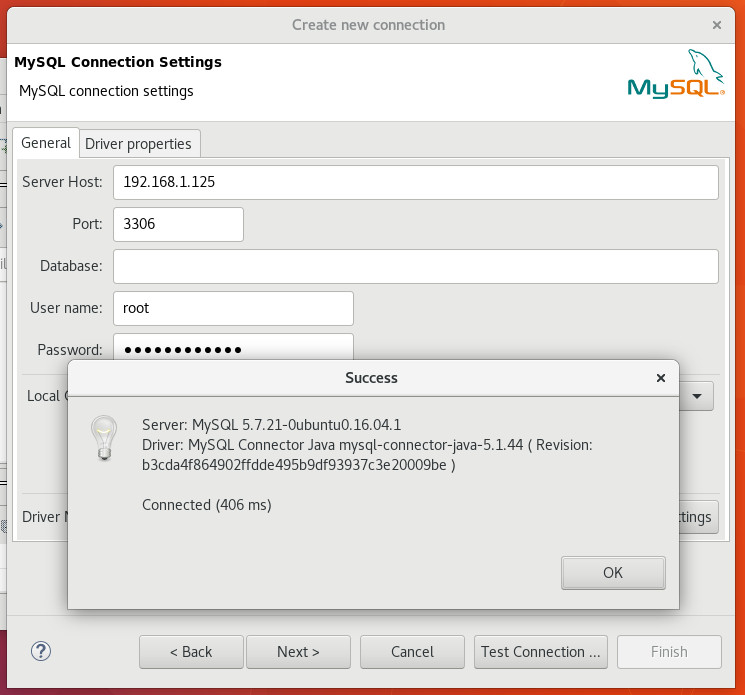
4. Click Next and fill in the password, you can test if everything works fine using the Test Connection option.
Client_plugin_auth Is Required Dbeaver Mysql 2017
5. If everything went well the test connection will succeed and you can click finish. On doing that you will be able to see the connection in the Database Navigator pane.
6. Sometimes you get an error public key retrieval is not allowed, in this case go Driver properties tab and in that tab you will be able to see a allowPublicKeyRetrieval property, set that to true. ( Note that AllowPublicKeyRetrieval=True could allow a malicious proxy to perform a MITM attack to get the plaintext password, so it is False by default and must be explicitly enabled.)
START, RESTART, STOP CONTAINERS
Start a docker container using docker start <containername>
Stop a docker container using docker stop <containername>
Client_plugin_auth Is Required Dbeaver Mysql Download
Restart a docker container using docker restart <containername>
Client_plugin_auth Is Required Dbeaver Mysql Pdf
Remove a stopped docker container using docker container rm <containername>
Feel free to write your thoughts as comments or email
writer@adevtalks.com